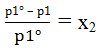The Colligative Properties of Solutions are :-
1. Relative Lowering of the Vapor Pressure
2. Elevation in Boiling Point
3. Depressions in Boiling Point
4. Osmosis
When a nonvolatile solute is added to a volatile solvent then the vapor pressure decreases.
The vapor pressure of a solution depends on the concentration of the solution irrespective of its identity.
The vapor pressure of a solvent is less than that of the pure solvent.
The vapor pressure is directly proportional to the mole fraction of the solution.
p1 = x1 p1o
The reduction in the vapor pressure:-
Δp1 = p1o – p1
Δp1 = p1o – x1 p1o
Δp1 = p1o (1 – x1)
The left side of the equation is called relatively lowering of vapor pressure and is equal to the mole fraction of the solute.
Here n1 and n2 are the number of moles of the solvent and solute respectively present in the solution.
The vapor pressure of a liquid increases with the increase in the temperature.
A liquid boils at the temperature at which the vapor pressure is equal to the atmospheric temperature.
For example, Water boils at 100 oC because at 100 oC the vapor pressure of water is
1.013 Bar (1 atmosphere) equal to the atmospheric pressure.